Acrylic monomers
Acrylic acid and its esters such as Methyl acrylate, Ethyl acrylate, Butyl acrylate and 2-Ethylhexyl acrylate, are known as basic acrylates. Most of the acrylates are flammable, volatile and colourless liquids.
Commercial Acrylic acid is produced by selective gas phase oxidation of propene. The crude acrylic acid is further purified to obtain different acrylic acid qualities of standard or ester grade to high purity grade acrylic acid. The purity of the acrylic acid produced usually exceeds 99.5%.
Acrylic acid and its esters are usually stabilised with inhibitors such as hydroquinone monomethyl ether (MeHQ). Because MeHQ is only effective in the presence of oxygen, the acrylic monomers must be stored under air or an atmosphere containing at least 5 Vol.-% of oxygen.
The stabilised monomers are generally stored below 25 °C. Acrylic acid should not be stored below 15 °C because acrylic acid crystallises.
 |
 |
 |
 |
The European Basic Acrylic Monomers group (EBAM)
EBAM is an industry association within Cefic comprising the manufacturers of acrylic acid and basic esters.
The EBAM members are:
- Arkema France: Arkema
- BASF SE: BASF
- Dow Europe GmbH: Dow
- Evonik Superabsorber GmbH: Evonik
- Synthomer a.s.
The group is managed by Konstantinos Sapounas, Sector Group Manager.
The EBAM Sector Group aims at:
- Supporting the sustainable and responsible use of acrylic acid and esters by
- Developing product stewardship programmes following the Responsible Care principles;
- Informing users about the safe handling of these products;
- Encouraging the safe and proper use of acrylates by developing and publishing appropriate technical information; see details in the “Relevant Studies and Literature” section;
- Providing Mutual Aid in case of transport incidents involving Acrylic monomers.
- Maintaining a high level of technical understanding by identifying and managing research into health and environmental effects and assessing risks in use;
- Developing data in support of the safe handling and safe storage of Acrylic monomers;
- Maintaining a PTZ (phenothiazine polymerisation inhibitor) locations database, which is part of EBAM’s commitment to provide emergency response services for acrylic monomers in Europe;
- Developing an Advocacy Program;
- Promoting the standing of the acrylics industry (acrylic acid and basic acrylic esters) in a socially responsible manner.
EBAM works closely with related Industry Associations such as:
– the Basic Acrylic Monomers Manufacturers
– the European Methacrylates Sector Group (MSG)
– the Methacrylate Producers Association Inc
– the European Polymer Dispersion and Latex Association (EPDLA)
– the European Disposables and Nonwovens Association (EDANA)
Product stewardship
Health & Safety
EBAM, based upon its members’ extensive experience in the safe handling of acrylic acid and esters, have prepared Safe Handling Guidelines for acrylic acid and the basic acrylate esters (MA, EA, BA and 2-EHA). These documents provide product stewardship advice for the safe storage, handling and use of these products. Safety Data Sheets (SDS), provided by each supplier, should be read and understood before ordering, storing and using acrylic monomers. See details in the “Relevant Studies and Literature” section.
Further information on acrylic monomers can be found in EBAM’s safe handling brochures below:
REACH regulation
The EBAM member companies are contributing to the activities of the Acrylate REACH Task Force within the framework of the REACH Legislation by the preparation of registration dossiers and support in the evaluation process.
The EBAM member companies follow the classification and labelling as outlined in the CLP Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 and in the REACH registration dossiers. This information is indicated in the table below:
| Substance Name: | Acrylic acid | Methyl acrylate | Ethyl acrylate | Butyl acrylate | 2-Ethylhexyl acrylate |
| EC Number: | 201-177-9 | 202-500-6 | 205-438-8 | 205-480-7 | 203-080-7 |
| CAS Number: | 79-10-7 | 96-33-3 | 140-88-5 | 141-32-2 | 103-11-7 |
| Index No: | 607-061-00-8 | 607-034-00-0 | 607-032-00-X | 607-062-00-3 | 607-107-00-7 |
| Classification: | Flam. Liq. 3 – H226 Acute Tox. 4 – H332 Acute Tox. 4 – H312 Acute Tox. 4 – H302 Skin Corr. 1A – H314 STOT SE 3 – H335 Aquatic Acute 1 – H400 Aquatic Chronic 2 – H411 |
Flam. Liq. 2; H225 Acute Tox. 3; H331 Acute Tox. 4; H312 Acute Tox. 4; H302 Skin Irrit. 2; H315 Skin Sens. 1; H317 Eye Irrit. 2; H319 STOT SE 3; H335 Aquatic Chronic 3 – H412 |
Flam. Liq. 2; H225 Acute Tox. 3; H331 Acute Tox. 4; H312 Acute Tox. 4; H302 Skin Irrit. 2; H315 Skin Sens. 1; H317 Eye Irrit. 2; H319 STOT SE 3; H335 Aquatic Chronic 3 – H412 |
Flam. Liq. 3; H226 Acute Tox. 4; H332 Skin Irrit. 2; H315 Skin Sens. 1; H317 Eye Irrit. 2; H319 STOT SE 3; H335 Aquatic Chronic 3; H412 |
Skin Irrit. 2; H315 Skin Sens. 1; H317 STOT SE 3; H335Aquatic Chronic 3 – H412 |
| Labelling | |||||
| Signal word: | Danger | Danger | Danger | Warning | Warning |
| Hazard pictogram: | GHS02 |
GHS02: flame |
GHS02 |
GHS02 |
GHS07 |
| Hazard statements: | |||||
| H226 H332 H312 H302 H314 H335 H400 H411 |
H225 H331 H312 H302 H315 H317 H319 H335 H412 |
H225 H331 H312 H302 H315 H317 H319 H335 H412 |
H226 H332 H315 H317 H319 H335 H412 |
H315 H317 H335 H412 |
H225: Highly flammable liquid and vapour.
H226: Flammable liquid and vapour
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
H331: Toxic if inhaled.
H332: Harmful if inhaled.
H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
H315: Causes skin irritation.
H319: Causes serious eye irritation.
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H335: May cause respiratory irritation.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H411: Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
H412: Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Links to the ECHA REACH dossiers:
Acrylic Acid: AA
Methyl Acrylate: MA
Ethyl Acrylate: EA
Butyl Acrylate: BA
2-Ethyl Hexyl Acrylate: EHA
The following legislations are closely monitored by EBAM and contributions are made as required:
Industrial Emissions Directive (IED):
The Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), adopted in 2010, fixes the rules for granting permits to operate industrial installations.
Water Framework Directive (WFD):
This Framework-Directive, published in 2000, has several objectives such as preventing and reducing pollution, promoting sustainable water usage, protecting the environment, improving the state of aquatic eco-systems and reducing the effects of floods and droughts.
Sustainability
Sustainability, also known as Sustainable Development, is a pattern of resource use that aims to meet human needs while preserving the environment so that these needs can be met not only in the present, but also for future generations.
Acrylic monomers have properties that constitute key assets in terms of sustainability.
In water-based paints and coatings, acrylate-based co-polymers provide good water resistance, low temperature flexibility, and excellent weathering and sunlight resistance. For construction products, acrylate chemicals offer properties such as strong adhesion, improved water resistance, ease of use, and increased durability. Some acrylate polymers also enable super-absorbency and flocculation. Finally, when used as molecular building blocks, acrylate-based monomers impart properties such as adhesion, flexibility, weather-ability, internal plasticisation, hardness control, abrasion protection, and resistance to oils and grease.
Life Cycle Assessment is a methodology that allows quantifying the environmental aspects and other potential impacts associated with a product, process or service from its beginning (cradle) until its end (grave) or re-use (cradle again). The LCA procedures are part of the ISO 14000 environmental management standards under ISO 14040 and 14044.
EBAM believes that LCA contributes to take more informed decisions through a better understanding of the human health and environmental impacts of products, processes and activities related to, or derived from, acrylic monomers. The EBAM member companies have joined efforts and work on widely agreeable standards concerning sustainability topics. To that effect, EBAM has established up-to-date LCA data for acrylic monomers. These results, together with the underlying methodology, are shared with other Industry organisations like Plastics Europe to ensure reliable and widely accepted sustainability data in the public domain. Beyond that, the Acrylic Monomers Industry is a strong advocate in supporting cradle-to-grave investigations for prominent application examples where acrylates prove to ultimately contribute to favourable sustainability footprint.
The LCA report (2024 update) is available on the Petrochemicals Europe website.
Global Product Safety Summaries
The International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA) has established the GPS Chemicals Portal to provide the public with easy access to science-based, reliable information on chemicals.
Easy access to information on acrylic monomers is provided via the above mentioned portal. The GPS Safety Summaries contained on the Portal provide the most relevant product safety information from companies on the chemical products they manufacture in a language that non-specialists will find easy to understand.
To date, more than 3.500 GPS Safety Summaries are available on the GPS Chemicals Portal, and ICCA member companies continue to post summaries to the site. Establishing a base set of information and publishing GPS Safety Summaries for their chemicals in commerce is part of the GPS commitment of ICCA member companies – and part of the chemical industry’s commitment to transparency.
Documents and Publications
EBAM has produced safe handling and storage guidelines. The purpose of these documents is to provide general information to all persons who use, handle, store, transport, or may otherwise be exposed to Acrylic Monomers and to advise on how to appropriately deal with the specific hazards, comprising health risks, flammability, the potential for untimely polymerisations and environmental risks.
- Working safely with acrylic acid and esters video (2020)
- Safe Handling and Storage Guidelines for Acrylic Acid, version 4 (2020)
- Safe Handling and Storage Guidelines for Acrylic Esters, version 3 (2016)
- Safe Handling and Storage Guidelines brochures are available from the EBAM member companies and Cefic.
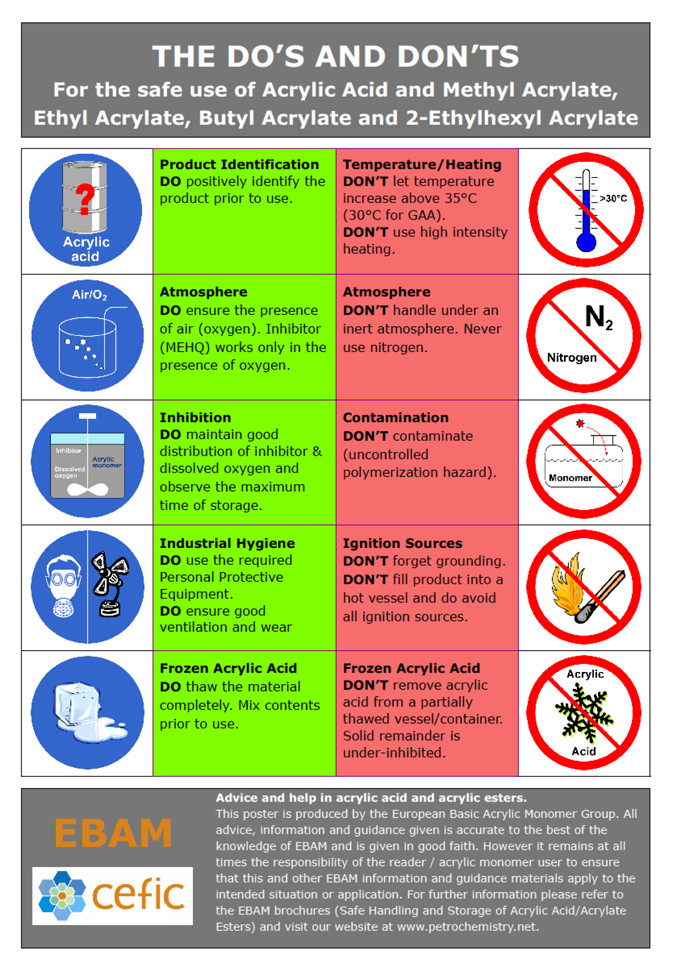
- The Do’s and Don’ts poster below was produced jointly by the EBAM member companies and Cefic. It is available in the following languages: CHN, CZ, DU, EN, FIN, FR, GER, GRE, HUN, IT, MAL, NOR, POL, POR, RUS, SP, SVK, SWE, TUR, UA.
- Best Practices such as: the BAMM publication entitled “Acrylic Acid: A Summary of Safety and Handling”:
- Recommendations and Guidelines for the use of dry disconnect couplings on transportation equipment for acrylic acid, methyl acrylate, ethyl acrylate, butyl acrylates and 2-ethyl hexyl acrylate.
- Recommendation when using combination load deliveries by trucks or barges for the transport of acrylic acid, methyl acrylate, ethyl acrylate, butyl acrylates and 2-ethyl hexyl acrylate.
- Recommendation when using bulk containers (IBCs) for the transport of acrylic monomers.
- Best Practice Guideline for Heating Stations (Updated – 2023)
- Incident with truck guidelines (Updated – 2023)
Other Information:
PTZ phenothiazine polymerisation inhibitor availability
Phenothiazine is a stabiliser for acrylic acid and acrylates that inhibits the polymerisation of monomers during the manufacturing process and provides protection during storage and shipment. Details can be found at the following web pages:
Allessa GmbH/WeylChem
https://www.chemicalparks.com/parks/45/seiten/default.aspx
Cytec Solvay Group:
PTZ: https://www.solvay.com/en/product/ptz-phenothiazine-prill
Monomer stabilization: https://www.cytec.com/businesses/additive-technologies/specialty-additives/industries-applications/monomer-stabilzation
Total Feuerschutz GmbH
RS · Roman Seliger
Chairperson
Chairman: Friedrich-Georg Martin, BASF-SE
Contact
Sapounas Konstantinos
Sector Group Manager
ksa (@) cefic.be